Abstract
Background
The immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) Thalidomide (THAL), Lenalidomide (LEN), and Pomalidomide (POM) have demonstrated potent anti-multiple myeloma (MM) activity both pre-clinically and clinically, and are accepted standards of care. LEN, POM and recently discovered analogs bind cereblon (CRBN), an E3 ubiquitin ligase, which confers gain-of-function recruitment of a specific set of target substrates, resulting in their proteasomal degradation with subsequent anti-proliferative and immunomodulatory effects. Although the list is likely incomplete, several cereblon-targeted substrates have been identified, including Ikaros (IK1), Aiolos (IK3), CK1a, and GSPT1. The specific subset of targeted substrates, and their respective extent and rate of degradation, determine the compound's net therapeutic benefit. In this study, we found activity in MM and related hematologic malignancies from a novel series of cereblon-binding small molecules known as Protein Homeostatic Modulators™ (PHMs™).
Results
Similar to the clinical IMiDs (THAL, LEN, and POM), the novel class of small molecules PHMs™ targets CRBN, acting as a molecule "glue" that promotes ubiquitination and subsequent proteosomal degradation of known select substrates such as CK1a, Ikaros, and GSPT1; and potentially, yet to be identified new clinically relevant substrates. In this study, we showed that while some PHMs have similar phenotypic and substrate degradation activity profiles to the clinical IMiDs, there are clear divergent profiles that are emerging. These activity profiles are derived from a multidimensional set of results such as cancer cell proliferation; cytokine and chemokine regulation; cellular differentiation; and specific substrate degradation. Using these profiles, we have identified potential clinical candidates for cancer and immune dysfunction. BTX252, BTX293 or BTX299 displayed the ability to promote degradation of GSPT1, Ikaros and CK1a. BTX304 is more potent in inhibiting IL-6 or TNFa in LPS stimulated PBMCs and degrading Ikaros than POM. The calculated IC50 for BTX306 is 0.0028 uM. BTX306-induced degradation of GSPT1 correlates well with its observed anti-proliferative activity. To identify potential PHM™ candidates for the treatment of relapsed and refractory MM, lead PHMs were tested on LEN resistant MM cell lines. To further understand and identify the clinical utility of the unique activity profiles of the various classes of PHMs, combination treatment of myeloma cell lines as well as drug resistant myeloma cell lines using standard-of-care chemotherapy (including the clinical IMiDs) will be presented.
Conclusion
We have shown that the PHMs, a novel class of CRBN-binding small molecules, have both similar activity profiles (phenotypic and substrate degradation) to the clinical IMiDs (LEN and POM) as well as unique activity profiles that are divergent to the clinical IMiDs. The lead PHMs, BTX306 and BTX304 have potential as a therapeutic agent in the treatment of MM and other hematological malignancies.
Methods
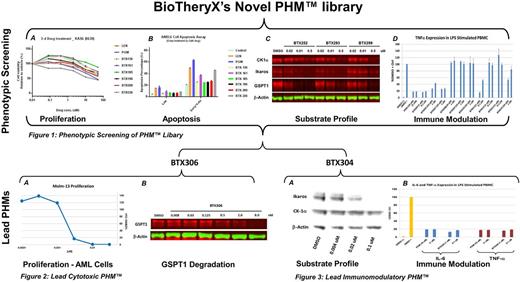
Phenotypic Screening of PHMTM Library. (A) Proliferation. The anti-proliferative activity of BTX136, BTX161, BTX185, BTX196, BTX200, or BTX226 was examined in KAS6 cells. DMSO, LEN and POM were included as controls. (B) Apoptosis. Examine the level of apoptosis in ANBL6 cells in response to treatment with BTX136, BTX161, BTX185, BTX196, BTX200, or BTX226 using flow cytometric assay. DMSO, LEN and POM were included as controls. (C) Target Substrate Profile. Western Blot analysis of a dose-response from Jurkat cells treated with DMSO, BTX252, BTX293 or BTX299 for 6 hrs. (D) Immune Modulation. The level of TNFa was measured in human primary PBMCs stimulated with LPS (100 ng/mL) for 18 hrs after dosing with Controls (DMSO or LPS only), POM or the indicated PHMTM.
Lead Cytotoxic PHMTM. (A) Cell proliferation assay of Molm-13 cells treated with BTX306 for 3 days. (B) Western Blot analysis of Molm-13 cells treated with a dose-response of BTX306 for 6 hrs.
Lead Immunomodulatory PHMTM. (A) Target Substrate Profile. Western Blot analysis of a dose-response from Jurkat cells treated with DMSO or BTX304 for 6 hrs. (B) The level of TNFa or IL-6 expression was measured in human primary PBMCs stimulated with LPS (100 ng/mL) for 18 hrs after dosing with Controls (DMSO or LPS only), POM or BTX304.
Zou: BioTheryX: Research Funding. Jones: BioTheryX: Research Funding. Sullivan: BioTheryX: Consultancy, Equity Ownership. Fung: BioTheryX: Consultancy, Equity Ownership. Richard: BioTheryX: Consultancy, Equity Ownership. Erdman: BioTheryX: Consultancy, Equity Ownership. Torres: BioTheryX: Consultancy, Equity Ownership. Chourasia: BioTheryX: Employment, Equity Ownership. Chan: BioTheryX: Employment, Equity Ownership. Mercurio: BioTheryX: Employment, Equity Ownership. Stirling: BioTheryX: Employment, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Orlowski: BioTheryX: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal